It’s March 14, 2015, which, in North America at least, makes it Pi Day (3/14/15), a day where people celebrate the most well-known mathematical constant with delicious baked goods and puns.
But in Middle-earth, the magical and engrossing world created by J.R.R. Tolkien as the setting for his tales of rings, hobbits, and adventure, Pi Day could coincide with the elven celebration of the Diptera! In Quenya, the ceremonial language of the high elves in Middle-earth, the word “fly” (in the entomological sense) translates directly to pí.

Translation and Tengwar courtesy of Lee Jaszlics (biologist, photographer, and Quenya aficionado)
Coincidentally, flies actually make their debut in the world of Middle-earth on March 15, 3019 (The Return of the King, Book Six, Chapter II – The Land of Shadow) as Frodo and Sam wander through a riverbed deep within Mordor. Tolkien writes:
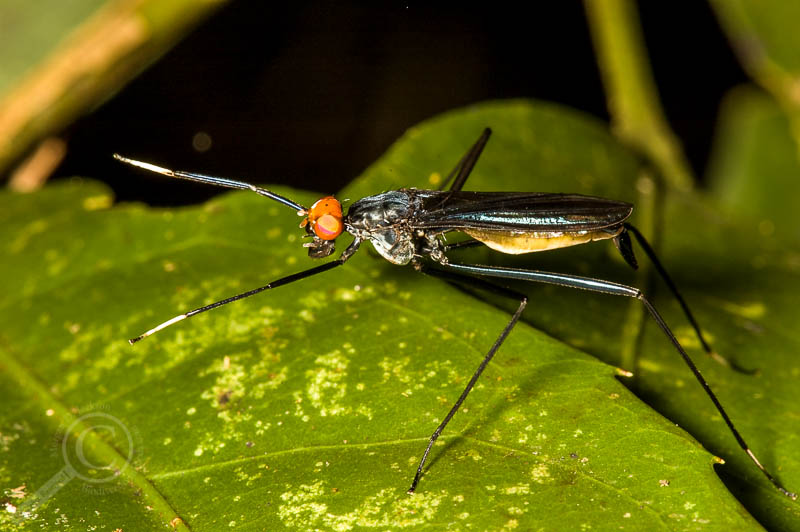
To their surprise they came upon dark pools fed by threads of water trickling down from some source higher up in the valley. Upon its outer marges under the westward mountains Mordor was a dying land, but it was not yet dead. And here things still grew, harsh, twisted, bitter, struggling for life. In the glens of the Morgai on the other side of the valley low scrubby trees lurked and clung, coarse grey grass-tussocks fought with the stones, and withered mosses crawled on them; and everywhere great writhing, tangled brambles sprawled. Some had long stabbing thorns, some hooked barbs that rent like knives. The sullen shrivelled leaves of a past year hung on them, grating and rattling in the sad airs, but their maggot-ridden buds were only just opening. Flies, dun or grey, or black, marked like orcs with a red eye-shaped blotch, buzzed and stung; and above the briar-thickets clouds of hungry midges danced and reeled.
The dancing midge clouds are easily explained, but I spent a lot of time trying to find a fly species that would fit Tolkien’s description. It turns out that “dun or grey, or black, marked like orcs with a red eye-shaped blotch” is a surprisingly rare combination in the Diptera. In fact, I couldn’t find any species of flies that could be described as dark with red splotches! Certainly there are species that are dark with red heads, including micropezids in the genus Scipopus, or signal flies in the genus Bromophila (as recently discussed by Piotr Naskrecki), and many flies are known for literally having red eyes (think of your friendly kitchen Drosophila), but unlike beetles, red blotches or spots seem to be rare in flies.
The only solution I could come up with that fit the general description and habitat of these Morgai flies was perhaps a species of Chrysopilus snipe fly (Rhagionidae), commonly called golden-backed snipe flies here in regular Earth. These flies have a blanket of magnificent golden pile on the top of their thorax, which can be brushed off giving the appearance of the Eye of Sauron (although they are certainly not blood suckers or pests). Perhaps under the evil influence of Sauron, a new species of Chrysopilus arose in Morgai, developed a taste for orc blood, and took to the air to reign terror from the skies.
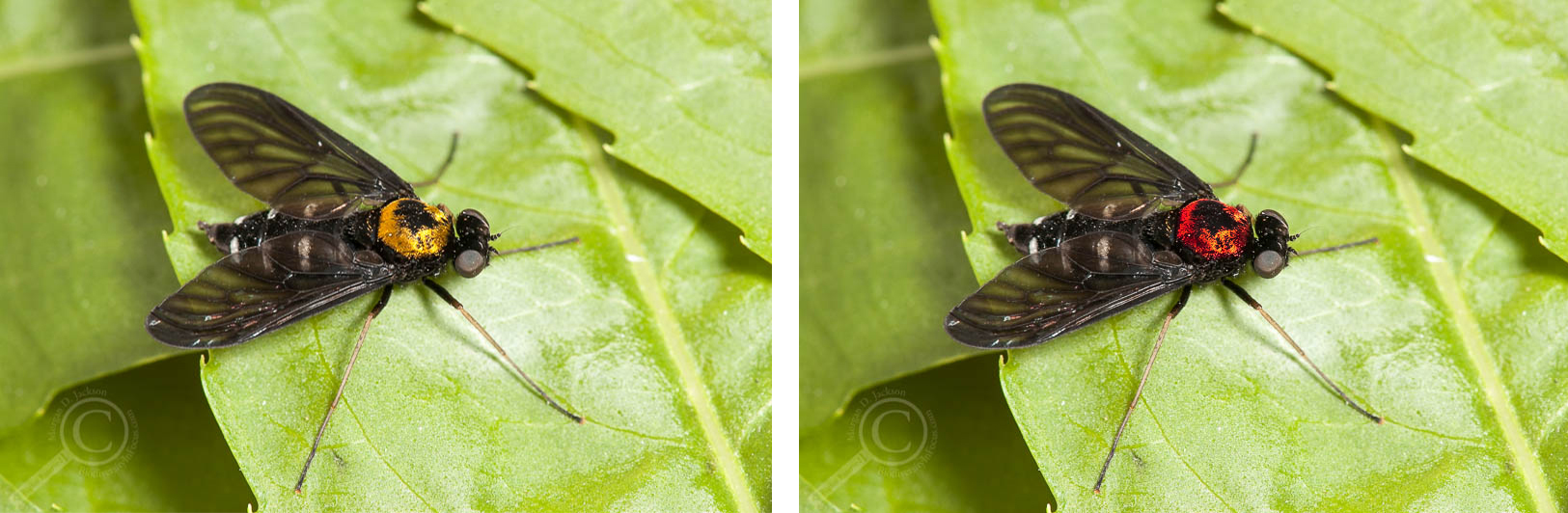

Chrysopilus thoracicus from Ontario on the left, with its Tolkienian cousin Chrysopilus “morgai” on the right
So on this Pí day, I hope you’ll not only herald the popular mathematical constants, but also the dipteran variables that make our natural history interesting, and our literary history magical.
Of course, the best possible way to celebrate would be to follow James Gilbert’s lead and make a Pí Pie for Pi Day. Mmmm, pie.
A Syrphus ribesii pork pie I made earlier #bakeyourstudyspecies – mimicry didn't help it that evening @SensoryEcology pic.twitter.com/saXqFuCEuU
— James Gilbert (@james_gilbert) March 11, 2015
Footnote: In the recent video game Middle-earth: Shadow of Mordor, Morgai flies were depicted as eusocial, living in paper hives, and able to drive off nearby orcs with a well-placed arrow. While I may be taking liberties with fly evolution to make a red, blood-sucking snipe fly, calling what are clearly social wasps “flies” gives WB Games a taxonomy fail index of 58. Now there’s some math for you.